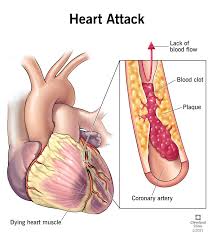
heart attack—medically known as a myocardial infarction—occurs when blood flow to part of the heart muscle is severely reduced or blocked. This can cause permanent damage or even death if not treated promptly. Early recognition and fast treatment are critical to survival and recovery.
What Causes a Heart Attack?
Heart attacks usually happen due to a blockage in one or more coronary arteries. This blockage is typically caused by:
- Plaque buildup (fatty deposits of cholesterol and other substances)
- Blood clots forming at the site of ruptured plaque
- Coronary artery spasms (less common)
Common Symptoms of a Heart Attack
Recognizing the signs early can save lives. Symptoms include:
- Chest pain or tightness (often in the center or left side of the chest)
- Pain or discomfort in arms, neck, jaw, back, or stomach
- Shortness of breath
- Sweating or cold sweats
- Nausea or vomiting
- Lightheadedness or sudden fatigue (especially in women)
What to Do During a Heart Attack (Emergency Steps)

- Call emergency services immediately (such as 911).
- Stay calm and still. Sit or lie down to reduce strain on the heart.
- Loosen tight clothing and help the person stay comfortable.
- Chew an aspirin (if not allergic), as it can help thin the blood.
- Start CPR if the person becomes unconscious and stops breathing.
Heart Attack Treatment Options
1. Medications:
- Aspirin: Prevents further clotting.
- Thrombolytics: Dissolve existing clots.
- Beta-blockers: Reduce heart workload and oxygen needs.
- ACE inhibitors: Improve heart function.
- Statins: Lower cholesterol levels.
2. Medical Procedures:
- Angioplasty and Stent Placement: Opens blocked arteries with a balloon and places a stent to keep it open.
- Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG): Bypasses blocked arteries using a blood vessel from another part of the body.
Heart Attack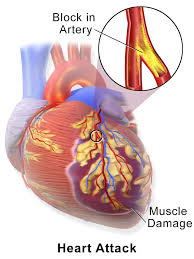 Recovery and Lifestyle Changes
Recovery and Lifestyle Changes
After a heart attack, long-term care and lifestyle changes are essential:
- Quit smoking completely
- Follow a heart-healthy diet (low in saturated fats, salt, and sugar)
- Exercise regularly under doctor supervision
- Manage stress through relaxation techniques
- Control blood pressure, cholesterol, and diabetes
- Attend cardiac rehabilitation programs
- Take prescribed medications consistently
Conclusion
Understanding heart attack symptoms, getting immediate help, and following through with proper treatment can greatly increase survival and recovery. If you or a loved one has risk factors for heart disease, regular checkups and preventive care are essential.









2 thoughts on “Heart Attack: Symptoms, Causes, and Effective Treatments”